Veeam Backup & Replication Best Practice Guide
Note: Although still relevant, the VSE tool described in this section will be taken down in the not-too-distant future in favor of the new VSE tool.
VSE navigation
The VSE interface as five pages:
- Dashboard — shows the results of the estimation
- Workloads — is where workloads are added to the estimation.
- Object — is where you can estimate object capacity and transaction costs
- Details — is where you can see an overview of all the workloads and a repository capacity breakdown
- Info — provides information on how to use the tool
Workloads
A workload defines a common set of requirements that need to be applied to a number of VMs or Agents (servers).
This allows for servers with different requirements to be added to the same estimation. For example, you may have servers with different retention or change rate requirements.
VM and Agent backups are supported. Agent backups do not contribute to the total proxy resource requirements. The VSE also assumes that Veeam Backup & Replication will manage all Agent backups.
Note: the growth added to servers and capacity in the calculation is linear not exponential.
Adding workloads
The VSE allows for an unlimited quantity of workloads to be added.
To add a workload press ‘new’ on the workloads page, this will bring up the ‘add workload’ form/page.
The add workload page is broken into three sections
- RvTools import
- Workload input
- Retention input
RvTools import
RvTools is a widely used tool available from https://www.robware.net/rvtools/ which can quickly and easily gather on a VMware environment.
These figures are taken from the ‘vInfo’ worksheet if you are not logged into the tool.
The VSE also only counts Powered On VMs.
The metrics used are:
- vInfo - VM (name)
- vInfo - Powered On VMs
- vInfo - In Use Capacity
If you are logged in then the following tabs are used:
- vPartition - VM (name)
- vPartition - Capacity MB
- vPartition - Free MB
The result of this is that the capacity figure that is used for the non-logged in is based on provisioned capacity. The logged in version is based on, where possible, the used capacity at a VM level.
The way the VSE does this is as follows:
- Each VM’s partition capacity is added together
- Each of the VMs that are in the vInfo tab are compared with the vPartition where this is a match the capacity figure is updated with the used capacity.
If a VM does not have VMware tools install and running, they will not appear in the vPartition tab. Using this method means that those VMs will still be included in the capacity total even if it is at the provisioned level.
Note that there is a button on the right-hand side of the screen labelled ‘import info’, this enables after a VMware tools import. It provides information on how the capacity figure calculated. It also provides a button to download a report on the VMs that were not updated with the partition information.
Workload
The workload form has several fields:
| Field | Details |
|---|---|
| Workload name | Name of the workload, we recommend it is something meaningful |
| Backup type | Select VM or Agent for the type of backup |
| Site | Select a site for the workload to be applied |
| Source Size (TB) | Source capacity that requires backup |
| Yearly Growth % | Yearly growth factor |
| Scope (Years) | The quantity of years the growth should be applied |
| Backup windows (hours) | Required Backup window |
| Daily change rate % | Estimated change rate for items in this workload |
| Reduction % | Reduction percentage from Veeam compression and deduplication |
| VM/Agent Qty | The quantity of VMs or Agents in workload |
| Use Per-VM | Select to use either Per-VM or Per-Job backups |
| Use ReFS/XFS? | Data reduction by using ReFS or XFS formatting |
Retention
Backup jobs has:
- Daily points - the short term retention points
- Weekly- Yearly points - GFS points
There have been changes in v4 which modified the behavior of GFS points, see section below for details.
Backup copy jobs, these are optional by recommended unless you have using cloud tier copies.
Backup copy jobs have an automatic 1-weekly enabled, this is to ensure that if Monthly or Yearly backups are added that there will not be the issue of a long backup chain.
Capacity Tier
Enabling the Capacity Tier field is the same as adding a ‘tier after’ within Veeam Backup & Replication, which sets the policy of when data should be tiered to the cloud aka a “Move” operation.
Enabling tiering in the workload for will affect the amount of storage held in the primary backup.
For example, the following workload:
- 30 Dailies
- Six monthlies
- One yearly
- Tier after 15 days
The following will be retained locally:
- 15 dailies
- Two weeklies
- Zero monthlies
- Zero yearlies
The VSE only supports Primary site tiering in the current form.
Note on inactive chains
As tiering (move) occurs on inactive chains, which are chains that are no longer active in the backup (full backup has occurred), it means that a minimum of seven days of local retention is required. This assumes that only one full backup occurs per-week, which is how the object estimate is designed. However, it is recommended to increase the retention to 14-days minimum to ensure local capacity requirements are met.
As the VSE does not restrict the number of daily restore points specified, but in the case of tiering the dailies should be set in multiples of seven. Similarly, with cloud tiering setting, it is recommended that this is also set in multiples of seven.
GFS only tiering is supported if the tiering points are higher than the daily restore points. For example: 14 daily backups and six monthlies with tiering set to after 14 will result in just the GFS points being uploaded.
V4 changes to GFS
RPC changes The addition of the RPC code is to increase accuracy of storage calculations and drive consistency across community tools.
It is important to note that unlike the original storage calculation, which was based on the GFS points being cumulative to the daily points e.g. 30 daily + 4 weekly = eight weeks total. The RPC code works on the GFS being inclusive of the daily points e.g. 30 daily + 4 weekly = four weeks as the weeklies will be within the daily points. You will need to therefore enter in 30 daily + 8 weekly to get the same result. It is the same as if you configured GFS in the VBR GUI.
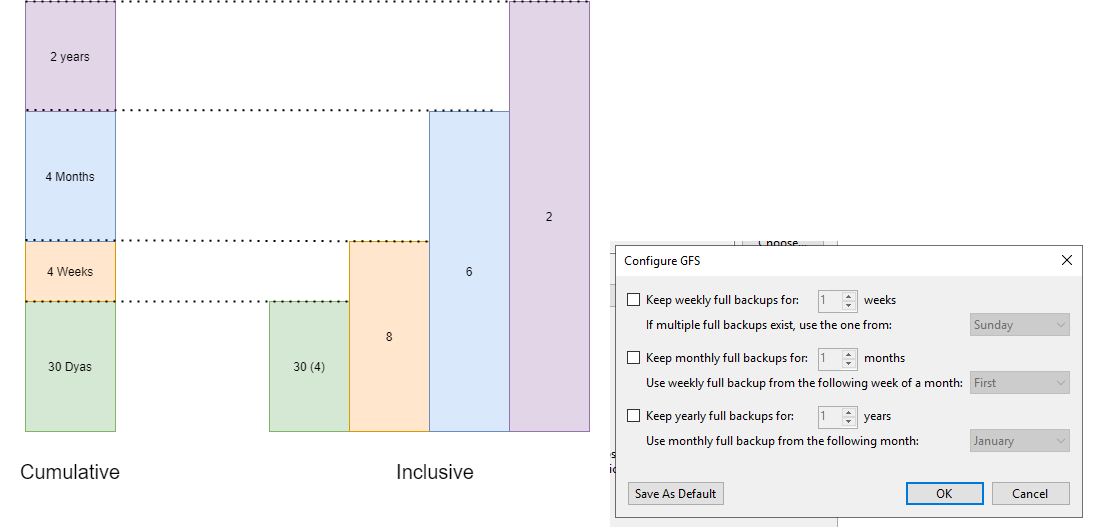
Also, unlike the original storage calculation, if you do not use ReFS/XFS formatting, the calculation will revert to a standard forward incremental chain with weekly fulls. The original code defaulted to forever-forward incremental.
Active / deactivate workloads
In the 4.3 update you are now able to activate and deactivate workloads on the main workload page:
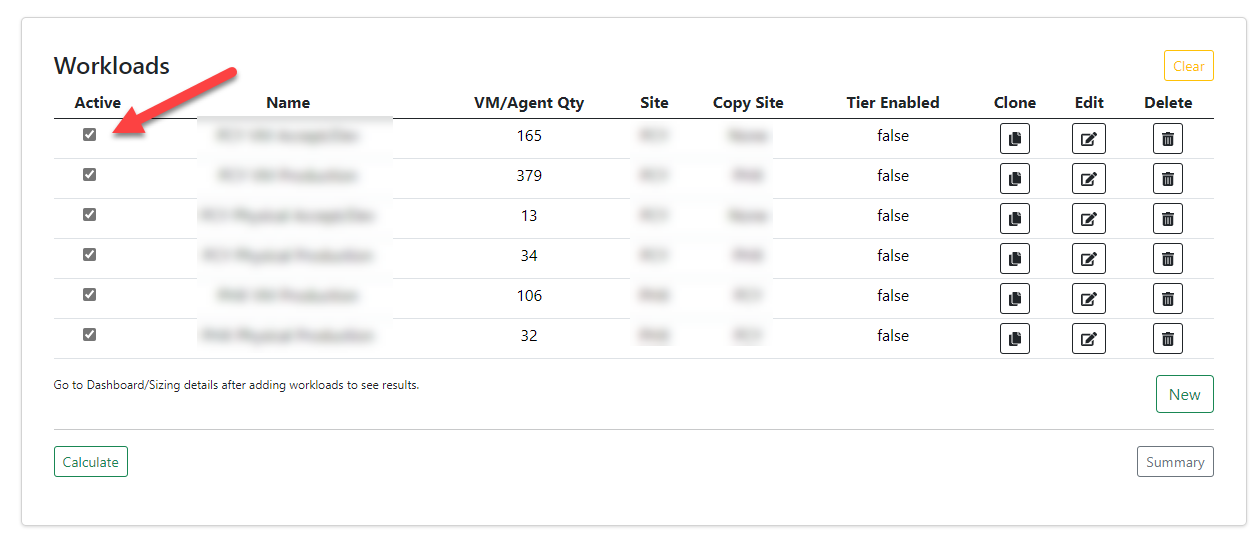
You will also see the relative activity at the top of each of the workloads when you create or edit them.
When the workload is deactivated it will not be included in the estimation. They will be included in the Excel output and configuration save but marked as inactive.
The feature was added to allow users to test out different scenarios without having to edit the workload(s).
Dashboard
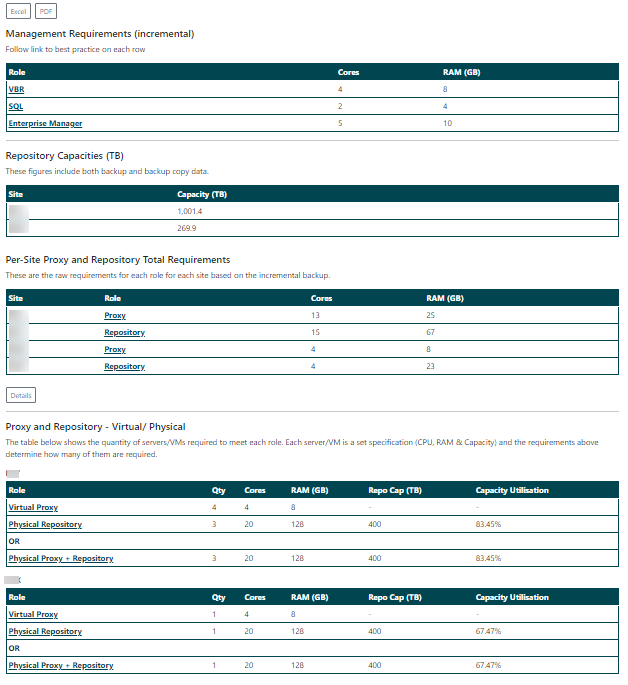
The dashboard provides the estimation based on the workloads you have inputted.
If the estimated requirements for the workloads do not meet the minimum requirements for Veeam, the minimum values will be shown.
The interface is broken up into several sections:
Management requirements
This section provides the estimated requirements for:
- The Veeam Backup & Replication server
- The configuration database
- Enterprise Manager
Repository capacities (TB)
This section provides the estimated capacity requirements per-site. The capacity includes backup copies from the other site.
Per-site proxy and repository total requirements
This section provides the total requirements for the proxy and repository services. The reason for this is to allow the user to make their own decisions on how those resources are provisioned and distributed.
The totals are broken down by site and in the case that no backups are specified on a site, the VSE will estimate the resource requirements based on the backup copy. The backup copy uses the window outside the main backup window for the estimation.
Proxy and repository - Virtual/ physical
This section is a guide to how a possible hardware solution could look.
The proxy and repository specifications are set by default at:
Virtual roxy:
- 4 cores
- 8GB RAM
Physical proxy or proxy and repo:
- 20 cores
- 128 RAM
- 400 TB
What the VSE does is compares all the requirements for the proxy and repository, then calculates the quantity of the above specs are required.
For example, proxy and repo total:
- 26 cores
- 72GB RAM
- 413TB capacity
Cores: 26 / 20 = 2 RAM: 72 / 192 = 1 Capacity: 412.66 / 400 = 2
Total physical proxy and repo required: Two
Details
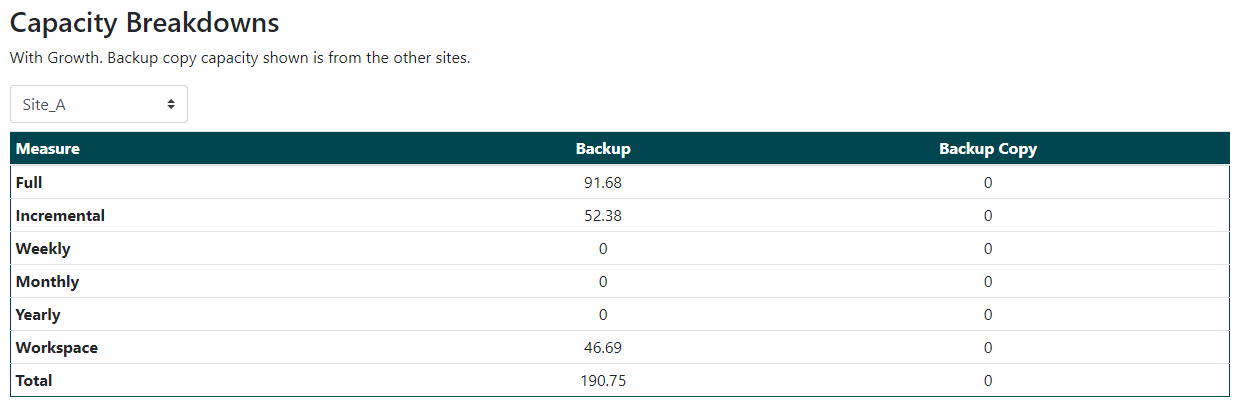
The details details page provides the following information:
- Break down of total protected resources
- Break down of the capacity requirements into individual loads
Object
Please see capacity tier section.



