Veeam Backup & Replication Best Practice Guide
Network Transport Encryption
What does it do?
Network transport encryption protects data “in-flight”. Communcation between Veeam components can be encrypted, even if job-level encryption has not been enabled. This is useful when the network between the source and target is not trusted.
How does it work?
Network encryption in Veeam Backup & Replication is controlled via the Global Network Traffic Rules.
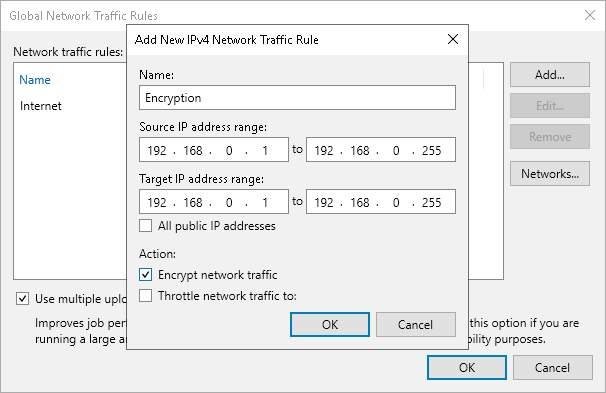
Once the traffic rule is in place:
- a dynamic key is generated by the backup server and communicated to each node over a secure channel
- the two components establish an encrypted connection between each other using this key
- all communications between these two components for that session will then be encrypted using this key
The key has a one-time use and it’s discarded once the session is completed.
When to use it?
Network transport encryption should be used if the network between two backup infrastructure components is untrusted or if the user desires to protect Veeam traffic across the network from potential network sniffing or “man in the middle” attacks.
By default, Veeam Backup & Replication automatically encrypts communication between two nodes if at least one has an interface configured (if used or not) that is not within the range of “Private Internets” as defined by IETF RFC 1918. Veeam also automatically uses network-level encryption for any connection with Veeam Cloud Connect service providers. However, Cloud Connect establishes a TLS 1.2 encrypted tunnel to the service provider in a different way.
To learn more about specific Cloud Connect encryption mechanism, checkout this page: How Veeam Cloud Connect Encryption works
Best Practices
- Enable encryption if network-level attacks are a security concern.
- Network-level encryption can use significant CPU resources, especially on the encrypting side (source) of the connection. Make sure that components have enough resources. Any CPU with AES-NI capability can offload encryption and reduce the amount of CPU resources required.
- If backup infrastructure components are running on a network that is using non-RFC1918 IP addresses but is still private and secure from attacks, consider using the following registry key to disable automatic network-layer encryption:
Path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Veeam\Veeam Backup and Replication Key: DisablePublicIPTrafficEncryption Type: REG_DWORD Value: 1 (default: 0)



