Veeam Backup & Replication Best Practice Guide
Veeam gateway server
The gateway paradigm
For any repository type that cannot host the Veeam transport agent, a repository gateway must be selected. The gateway server receives data from the proxies, optionally decompresses data, builds the backup files and writes them to storage.
The gateway selection can be static or automatic. Each option has pros and cons that are explained below. In any case the gateway selection must be studied carefully since it impacts the overall behavior of the Veeam workload.
Gateway compute sizing
The gateway compute can be considered as equivalent to the standard repository compute. The recommendation is to apply a 3:1 ratio against the proxy compute calculation based on the number of parallel tasks required to fulfill the backup window.
One important thing to keep in mind while sizing the repository gateway is that it might also be used to handle secondary tasks such as backup copy jobs.
If the gateway is not coupled with the proxy its sizing is the same than for any simple repository.
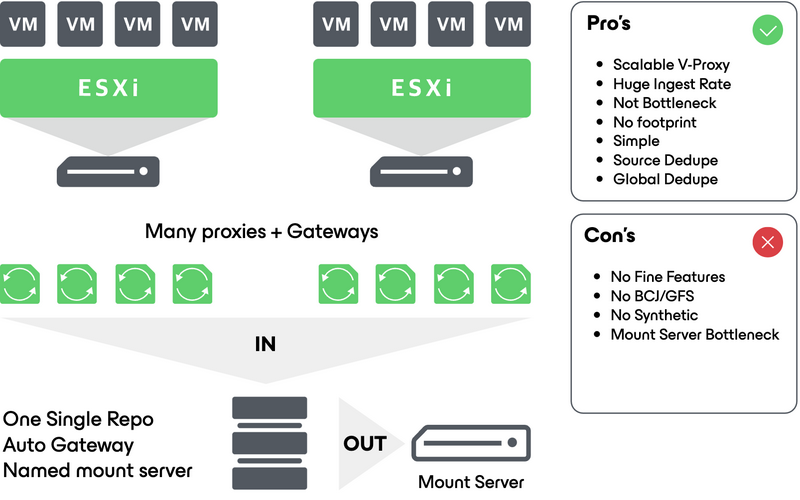
Automatic gateway selection
Please refer to the helpcenter to understand how gateway selection works.
It must be used with caution if backup copy job or synthetic operations are used, because in such cases the mount server configured will be the only component handling these operations, potentially creating a bottleneck. This is of course also true for agents backup as the backup server itself will then be elected as the gateway.
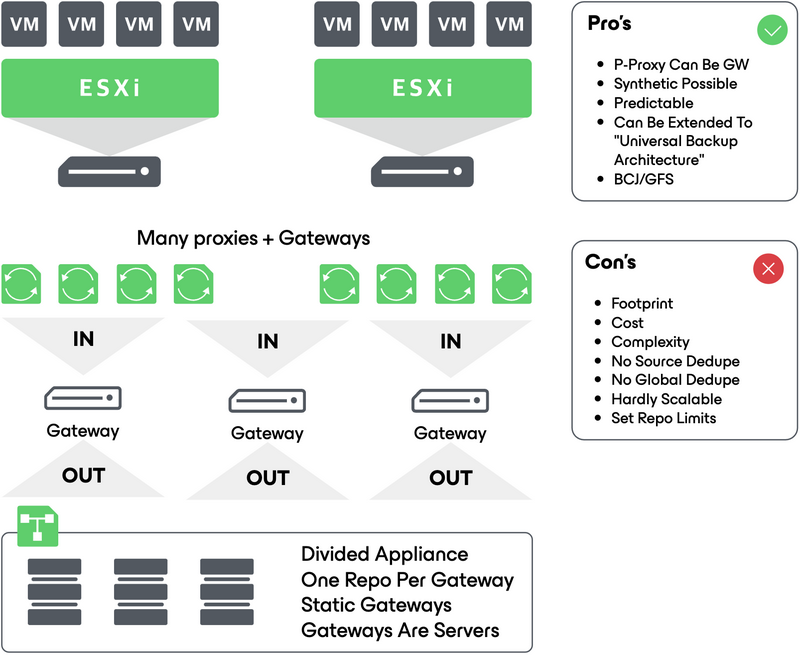
Static gateway
A static gateway setup will allow more predictable results than an automatic gateway setup, but it may not satisfy the performance needs regarding enterprises, like storage due to compute limitations. For example, DataDomain or StoreOnce storage would accept thousands of parallel connections while a static repository could only serve tens of them due to CPU limitations. This is especially true if the gateway is virtualized, usually limited to a reasonable maximum of eight cores. In such conditions the storage might be underutilized.
To overcome this limitation, a good option is to split the storage in many repositories, stacking multiple gateways in front of it.
Compared to automatic gateway, such configurations will allow the use of synthetic operations or backup copy jobs, but will be less flexible.
Typical drivers for automatic vs. static gateway
For huge scale-out configurations where only backup and restore matters, automatic gateway selection with virtual machines as proxy and gateway servers is the most effective way in terms of performances and scalability. Such configurations can easily saturate the storage with no additional physical footprint. Keep in mind that using active full backups might be desirable if the mount server comes to saturation while performing synthetic operations.
Automatic gateway selection with virtual proxies configuration:
If attention has to be paid on backup copy jobs, LAN free backup or if backup of agents must be intensely used, the static gateway configuration would be preferred for its predictability.
Static gateway configuration: