Veeam Backup & Replication Best Practice Guide
Instant VM Recovery (IVMR)
Usually reserved for the guests requiring the best possible RTOs, the Instant Recovery process is read intensive and its performance is directly related to the performance of the underlying repository.
Multiple Instant Recovery sessions can be started in parallel, it is also possible to use this feature along with any Veeam backup, including Veeam Agents, Hyper-V VM’s, Nutanix AHV VM’s, oVirt VM’s, Proxmox VE VM’s as well as cloud native backups from Veeam Backup for Azure, AWS and Google Cloud.
Very good results can be obtained from standard drive repositories (sometimes even offering faster boot time than the production guest) while deduplication appliances might be considered carefully for such kind of use. Keep in mind that when working on its backup files to start the guest, Veeam Backup and Replication needs to access the metadata, which generates random small blocks read pattern on the repository.
Write redirections
Before it is started, the VM is snapshotted to redirect all written data to a separate disk file. Once booted, the guest will read existing blocks from the backup storage and write/re-read new blocks on the configured storage, whether being a datastore or a temporary file on the Veeam Mount Server local drive (Typically in C:\ProgramData\Veeam\Backup\IRCache\ but any disk may be used depending on the available free space).
To ensure consistent performance during the IVMR process, it is recommended to redirect writes on the same datastore where the instant-restored VMs will eventually be moved. This will not only improve the performance of the restored VM but it will also reduce the network traffic going through the Veeam Mount Server.
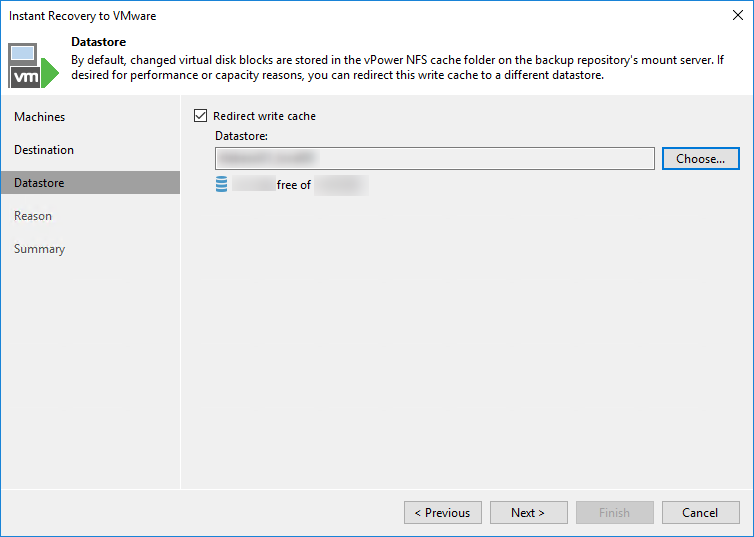
Redirecting the write cache on the target datastore will also reduce the amount of free space that needs to be available on the Mount Server as the virtual machine swap file (.vswp) will be created on the datastore. The swap file has the same size as the guest OS’ memory (minus the memory reservations if any). Keep this in mind, when planning a multiple Instant Recovery or powering on a VM configured with a high amount of RAM.
When write cache redirection is not used, the free disk space on the Veeam Mount Server must be equal to or greater than the total size of all swap files for the VMs undergoing Instant Recovery, plus an additional 10% of their disk sizes to accommodate all changes.
Be aware that when write cache redirection is enabled, a Quick Migration will be triggered when Migration to production is initiated in the VBR console.
Finalizing the process
The Instant Recovery process is a temporary state that requires to be finalized. The available options are:
- Use VMware Storage vMotion to migrate the restored VMs to the desired datastore without any downtime
- Use Veeam Quick Migration feature, if VMware Storage vMotion is not available
- Stop Session : the restored VM will be unpublished without any change to the original restore point
Another option that might be considered would be to use a replication job to create an additional copy of the instant-recovered VM and plan a failover at a later time or during the next maintenance window, then stop the IVMR session. Of course, if for any reason that scenario was to be chosen, it would require more manual operations, proxy tasks and I/O.
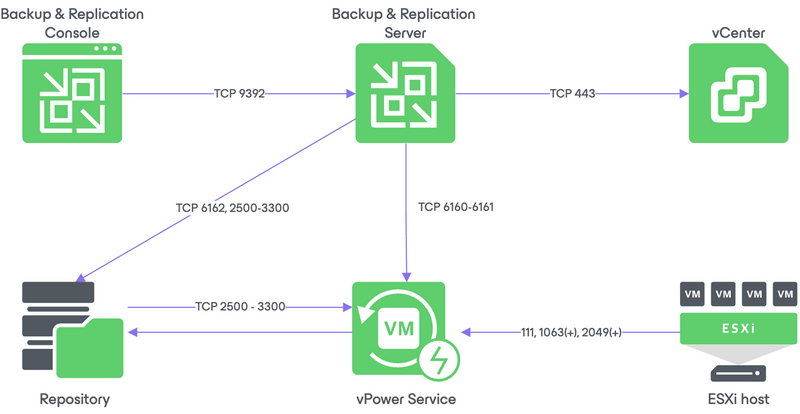
Network ports
Below the network ports required to the Instant VM Recovery and the communication flow between all the involved components: