Veeam Service Providers Best Practice Site
Design
The Off-Site Backup service can be architected using different approaches, each with distinct characteristics for performance, cost, and operational complexity.
In principle, the off-site backup infrastructure consists of the following components:
Service Provider side:
- Cloud connect gateways as a front end connection endpoint
- Veeam Cloud Connect server (VBR) as a central infrastructure management piece
- Database server (for VBR configuration and metadata)
- Backup storage
- Service Provider backend infrastructure: firewalls, network, DNS etc.
Customer side:
- Veeam Backup & Replication or Veeam Agents
In addition, for a fully managed service it is recommended to deploy Veeam Service Provider Console for streamlined billing and tenant onboarding. Refer to the MSP section for the VSPC design principles.
Backup storage
Arguably, the most important component to be designed and planned properly is the backup repository. There are three distinctly different ways how service provider can offer off-site storage:
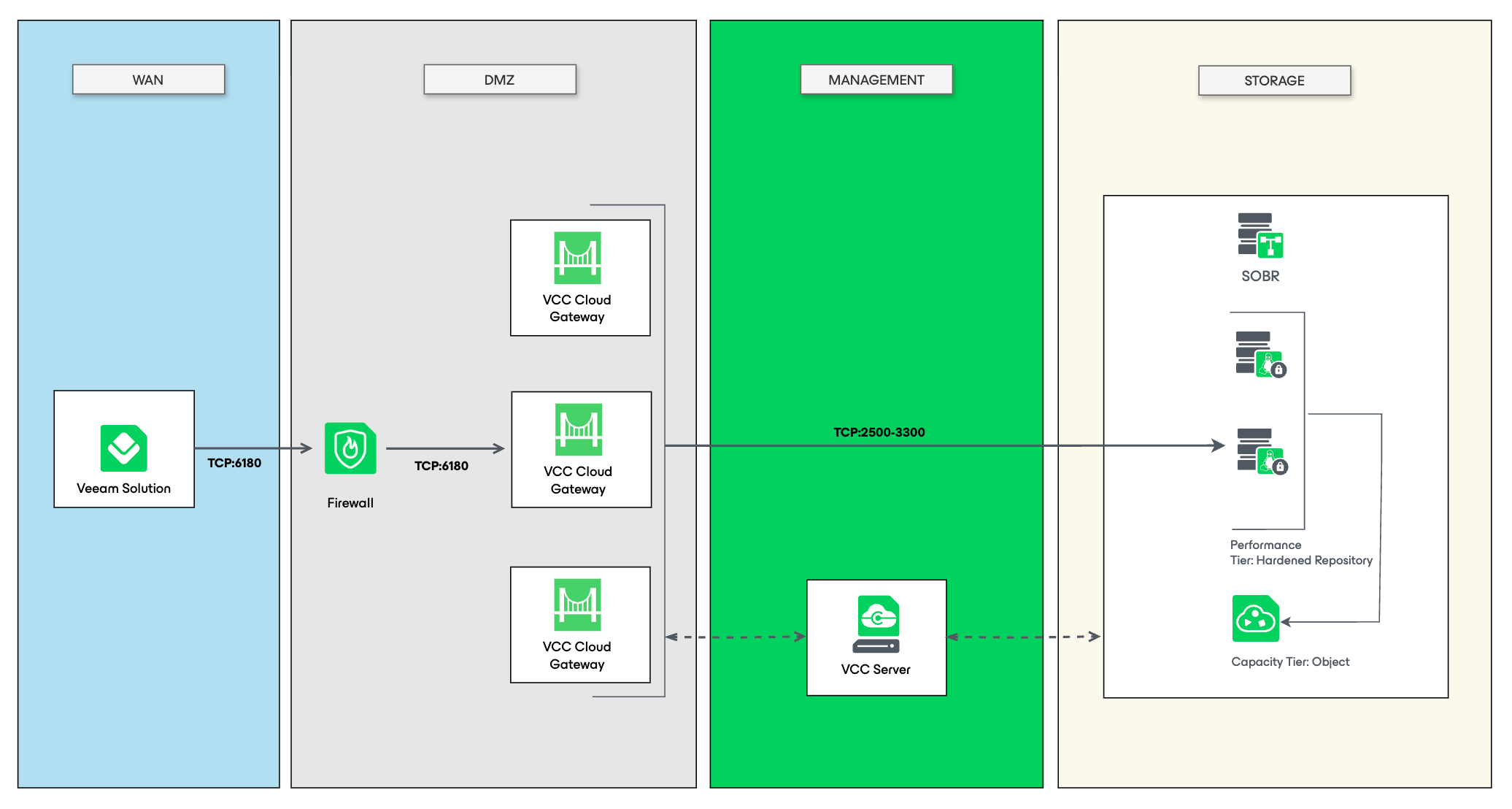
1. Traditional Cloud Connect deployment
All the backup traffic from the tenant traverses the Cloud Connect Gateways. Backup storage is abstracted and presented to the tenant as a generic Cloud Repository with a quota. Given that immutable storage and data redundancy are critical requirements in data protection scenarios, it is recommended to implement Veeam Hardened Repository (VHR) or on-premises S3-compatible object storage as the primary landing zone. This can be further enhanced by configuring capacity and archive tiers within a Scale-out Backup Repository (SOBR) to provide secondary data copies and long-term retention capabilities.
This approach provides maximum control but requires storage and network infrastructure investment and capacity planning.
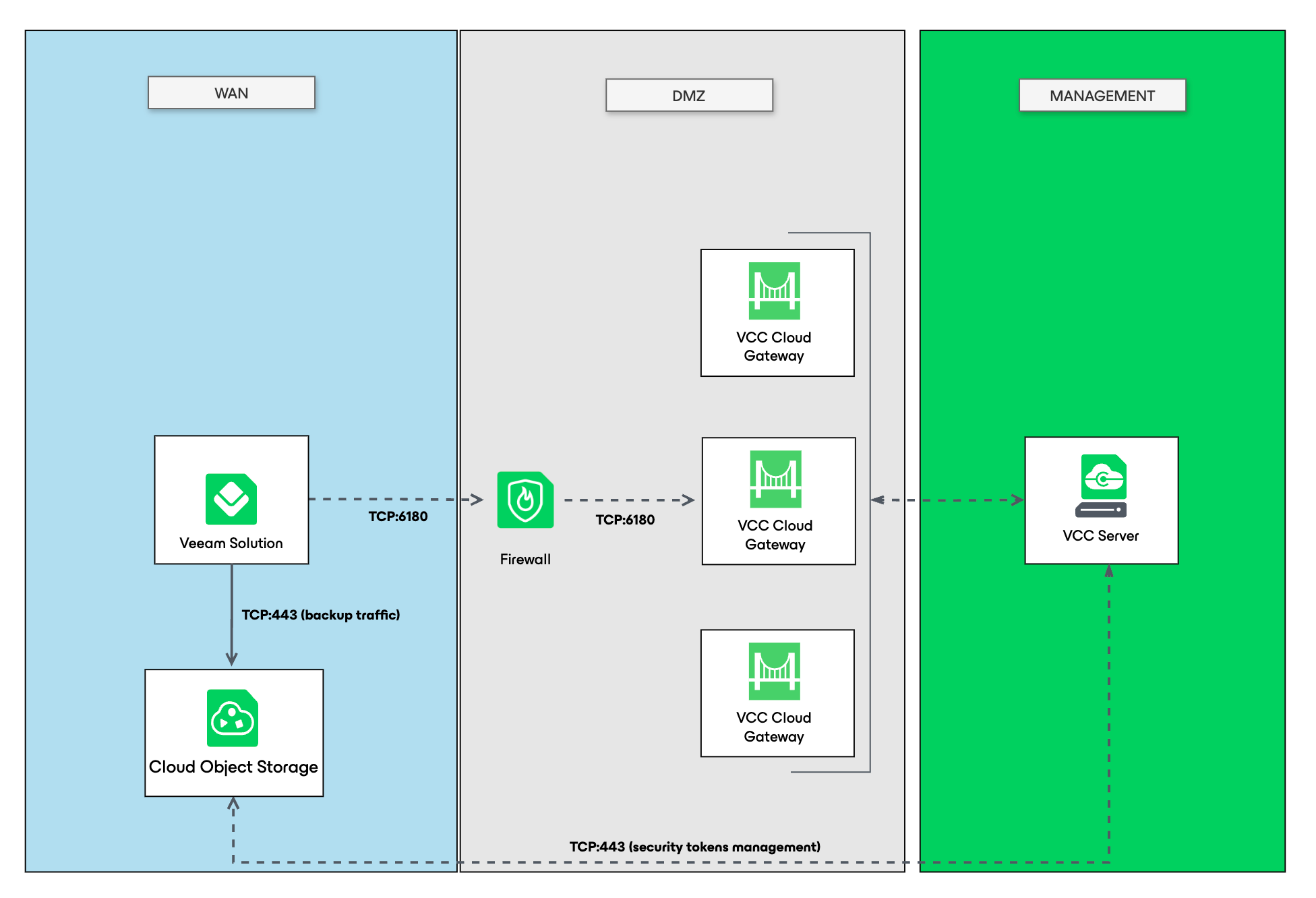
2. Object storage directly exposed to the customer, managed via Cloud Connect
Always check the supported object storages first. This architecture employs Secure Token Services (STS) for S3-compatible storage or Azure Shared Access Signature (SAS). Since backup data flows directly to object storage without traversing the service provider’s infrastructure, this scenario supports significantly higher concurrent task volumes with minimal impact on provider resources. Additionally, there is no requirement to create per-customer buckets or storage accounts since backups are securely isolated through STS/SAS token-based access controls.
This hybrid model is recommended for environments that need to support hundreds of Veeam Agents. It reduces infrastructure costs and increases scalability.
3. Object storage repository directly exposed to the customer, managed via the local VBR or Agent.
A dedicated S3 bucket or Azure Blob is provided to a tenant without Cloud Connect components. This approach mirrors the MSP scenario, where the service provider primarily handles end-user VBR administration and provisions per-tenant storage, optionally utilizing Cloud Connect as a secure communication channel for the Service Provider Console. Object storage backup repositories can be provided through three main options:
- Veeam Data Cloud Vault: Secure, pre-configured and fully managed backup storage
- Public cloud storage: AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage, or other hyperscaler offerings
- On-premises object storage: Storage-as-a-Service hosted at the service provider site using S3-compatible solutions.
This approach provides maximum support for different backup job types.
Resources for managed backup design
For details on each scenario, please refer to the following resources:
For Cloud Connect infrastructure:
- Veeam Cloud Connect Reference Architecture - Architecture section
- Veeam Cloud Connect - User Guide
- Scenario 2: Configuring Object Storage Secure mode (STS/SAS) whitepaper
Veeam Service Provider Console resources:



